How many watts does a freezer use is a quiet question many homes never ask.
Freezers work day and night, silently shaping electricity bills.
Understanding their power use brings clarity, not worry.
A freezer feels simple, yet its energy story runs deep.
Knowing this story helps households plan better and live lighter.
Understanding Freezer Electricity Use
A freezer does not run constantly at full power.
It cycles on and off to maintain cold temperatures.
Electricity use depends on size, design, and environment.
Smaller freezers use less power, yet run frequently.
Larger freezers use more watts but cycle less often.
Both designs balance cooling needs differently.
Freezers consume power mainly through compressors and fans.
Insulation quality plays a silent but powerful role.
A well-insulated freezer saves electricity every hour.
A poorly insulated one struggles endlessly.
Ambient room temperature also affects energy use.
Hot surroundings force the freezer to work harder.
Placement matters more than most people realize.
A calm, cool corner reduces power demand naturally.
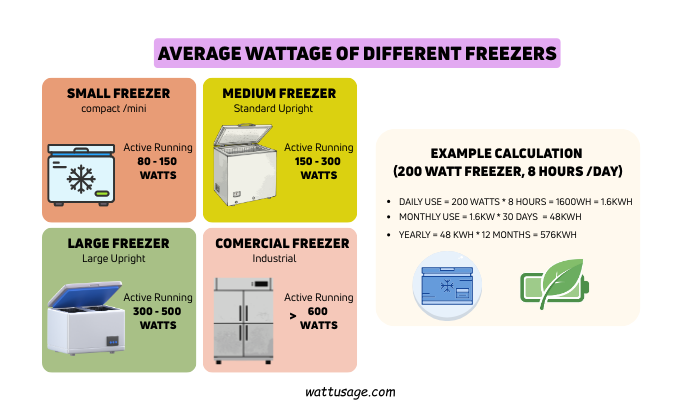
Average Wattage of Different Freezers
Small freezers usually consume 80 to 150 watts while running.
Medium freezers often draw 150 to 300 watts.
Large chest or upright freezers may use 300 to 500 watts.
Commercial or deep freezers can exceed 600 watts.
However, these numbers reflect active running periods.
Actual daily use depends on cycling frequency. A freezer may run only a few hours daily. This keeps total electricity use lower than expected.
For example, a 200-watt freezer running eight hours daily:
Daily use equals 1.6 kWh.
Monthly use equals 48 kWh.
Yearly use equals 576 kWh.
Electricity costs remain manageable for most households.
Efficiency improves with modern freezer designs.
Daily, Monthly, and Yearly Consumption
Freezers consume electricity quietly but consistently.
This makes long-term understanding important.
Daily consumption varies with door openings.
Frequent opening allows cold air to escape. The freezer compensates by running longer cycles. This increases electricity use gradually.
A freezer used carefully consumes less energy. Mindful habits reduce waste without effort.
Monthly usage often ranges between 30 and 100 kWh. Yearly consumption usually stays between 400 and 800 kWh.
Energy-efficient models stay at the lower end. Older models often consume more than expected.
Replacing an old freezer can save money long-term. Savings appear slowly but steadily.
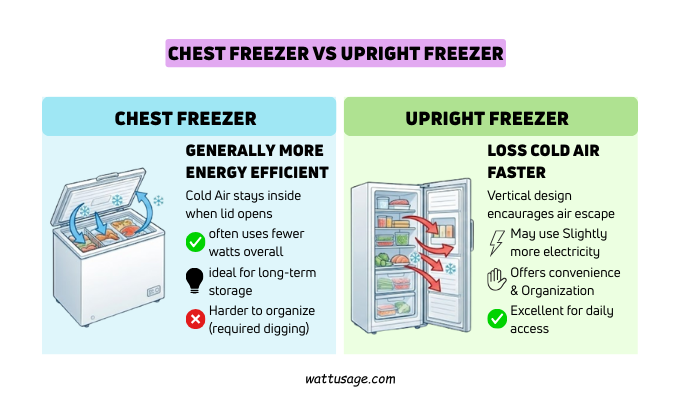
Chest Freezer vs Upright Freezer
Chest freezers are generally more energy efficient. Cold air stays inside when the lid opens.
Upright freezers lose cold air faster.
Their vertical design encourages air escape. Chest freezers often use fewer watts overall. They are ideal for long-term storage. Upright freezers offer convenience and organization. They may use slightly more electricity.
Choice depends on lifestyle, not just wattage. Efficiency should serve daily comfort.
Factors That Increase Freezer Power Use
Several factors quietly raise electricity consumption.
Poor insulation causes constant cooling loss. Worn door seals leak cold air unnoticed.
Overloading blocks proper air circulation. Under-loading reduces thermal stability.
High room temperatures increase compressor workload. Dirty coils trap heat inside the system.
Old freezers lack modern efficiency features. Manual defrost models consume more power.
Each small issue compounds over time. Awareness helps prevent unnecessary energy loss.
Freezer Wattage Comparison Table
| Freezer Type | Average Watts | Daily kWh | Monthly kWh | Yearly Cost Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Freezer | 100 W | 0.8 | 24 | Low |
| Medium Freezer | 200 W | 1.6 | 48 | Moderate |
| Large Freezer | 400 W | 3.2 | 96 | Higher |
| Commercial Freezer | 600 W | 4.8 | 144 | Highest |
These values vary by usage and environment. Efficient habits lower real costs significantly.
How to Reduce Freezer Electricity Use
Keep the freezer full but not crowded.
Frozen items help maintain internal temperature.
Avoid frequent door openings. Plan what you need before opening.
Clean coils every few months. This allows heat to escape easily.Check door seals regularly. Replace damaged seals immediately. Set proper temperature levels.
Over-freezing wastes electricity.
Place the freezer away from heat sources. Cool surroundings reduce energy demand. Use energy-efficient models when upgrading. Long-term savings justify initial cost.
Environmental Impact of Freezer
Freezers contribute steadily to household energy use.
Small reductions create meaningful impact. Efficient freezers lower carbon footprints. Responsible use supports environmental balance.
Choosing wisely protects both wallet and planet. Simplicity leads to sustainability.
Conclusion
How many watts does a freezer use depends on size, design, and habits.
Most household freezers consume between 80 and 500 watts while running.
Actual electricity use depends on cycling, environment, and maintenance. Efficient models and mindful use reduce long-term costs.
Understanding freezer energy use brings calm control. Small awareness creates lasting savings.
FAQs
Q1: Does a freezer run all day?
No, it cycles on and off as needed.
Q2: Are chest freezers more efficient?
Yes, they usually retain cold air better.
Q3: Does freezer size affect wattage?
Yes, larger freezers generally use more watts.
Q4: Can an old freezer increase bills?
Yes, older models are less energy efficient.
Q5: Is it expensive to run a freezer yearly?
Most household freezers remain affordable yearly.
