“What color is electricity?” is a fascinating question that mixes science and curiosity.
When we see sparks, arcs, or lightning, electricity seems to glow in bright colors.
Understanding what color electricity is helps explain its behavior, energy, and physical properties.
Electricity itself is invisible, but the glow we see comes from ionized gases and energy reactions. Curious minds often wonder why sparks look blue or yellow, while lightning flashes white.
Why Electricity Appears Coloured
Electricity passes through different materials, exciting electrons in the process.
When electrons jump energy levels, they release photons, which we perceive as light.
The color we see depends on temperature, material, and ionized gases involved in conduction. For example, sparks from metal wires appear blue-white, while high-voltage arcs may look purple or yellow.
Lightning contains nitrogen and oxygen, producing brilliant white or bluish flashes in the sky.
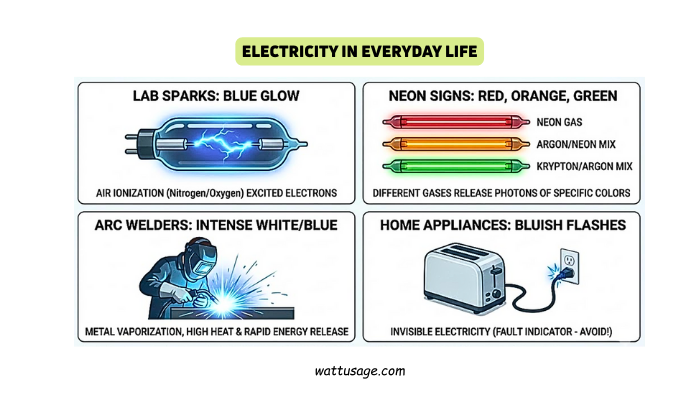
Electricity in Everyday Life
Electrical sparks in labs often glow blue due to air ionization.
Neon signs emit red, orange, or green light depending on the gas used. Arc welders produce intense white or blue sparks because metals vaporize and heat rapidly.
Even your home appliances create invisible electricity, but small sparks may show bluish flashes during faults.
Scientific Explanation
Electricity is the flow of electrons, which has no inherent color.
The colors we see are due to energy release when electrons interact with atoms or gases. High-energy electrons create short-wavelength blue light, while lower-energy interactions produce yellow or red.
The medium electricity passes through determines spark color: air, water, neon, and metals differ.
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, often glows brightly under electrical discharge.
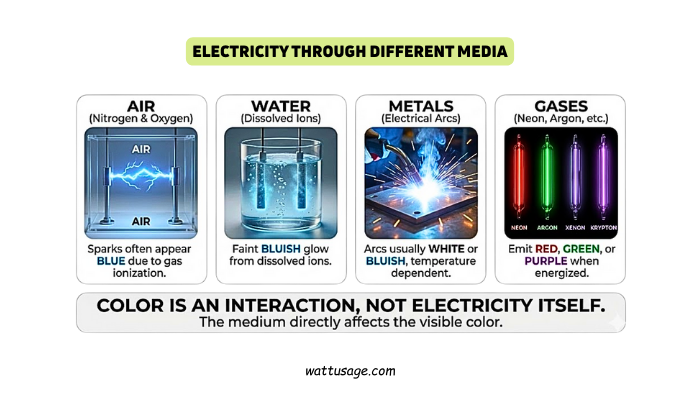
Electricity Through Different Media
Air: Sparks often appear blue due to nitrogen and oxygen ionization.
Water: Dissolved ions create faint bluish glows when electricity passes through.
Metals: Electrical arcs are usually white or bluish, depending on temperature.
Gases: Neon, argon, xenon, and krypton emit red, green, or purple when energized.
The medium directly affects electricity’s visible color, showing that color is an interaction, not electricity.
Safety Considerations
- Visible sparks may seem beautiful, but electricity is extremely dangerous.
- High-voltage arcs can cause severe burns or fatal shocks.
- Always use insulated tools and follow electrical safety guidelines during experiments.
- Never touch live wires or exposed electrical components, even if the sparks look small.
- Household sparks, like from switches, are usually low power but should not be ignored.
The Science Behind the Glow
Electricity excites atoms, which release photons during electron transitions.
Different energy levels produce photons of different wavelengths, which appear as colors. The intensity and frequency of energy determine whether the glow looks blue, red, or white.
This principle explains neon signs, sparks, welding arcs, and lightning.
By understanding electron behavior, we can predict electricity’s apparent colors in controlled experiments.
Fun Facts About Electricity Colors
- Lightning can appear blue, white, yellow, or even purple depending on atmospheric conditions.
- Neon lights demonstrate that electricity can make gases glow in vivid colors.
- High-voltage arcs look bright white or blue due to extreme heat energy.
- Static electricity sometimes produces faint blue sparks when discharged.
Understanding these colors makes electricity less mysterious and more visually fascinating.

Conclusion
Electricity itself has no color, it is invisible to the naked eye.
The colors we observe come from interactions with gases, metals, and plasma. Sparks, lightning, and neon signs create beautiful flashes of blue, white, yellow, or red. Electricity’s color is therefore a reflection of energy release and medium properties, not electricity itself.
Observing electricity teaches us about energy, light, and matter in a visually captivating way.
FAQs
Q1: Can electricity itself be colored?
No, the visible colors are caused by ionized gases or materials, not electricity itself.
Q2: Why do sparks from metals appear blue?
High-energy electrons excite air molecules, producing blue-white light in the process.
Q3: Why is lightning white or blue?
Lightning heats air to extreme temperatures, ionizing nitrogen and oxygen to emit white or blue light.
Q4: Can we control electricity color in experiments?
Yes, using different gases like neon, argon, or xenon changes the visible glow.
Q5: Does color indicate electricity danger?
No, color is only a visual effect. All high-voltage electricity is potentially dangerous.
