When you ask how many watts does a laptop use, you might wonder about your electricity bill.
Most people think laptops are heavy power users like big appliances.
The reality is gentle and simple: laptops generally use much less electricity than many expect.
Understanding how many watts a laptop uses helps you plan energy use and costs.
We will explore real data, typical ranges, cost estimates, daily use, and ways to save power.
This guide uses real measurements and friendly examples to keep everything clear.
What Laptop Power Use Actually Means
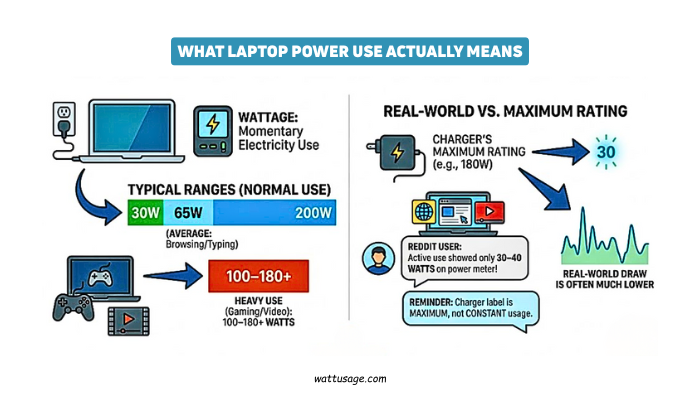
Laptop power use refers to the amount of electricity your device draws from the outlet.
This is usually measured in watts, which tells how much electricity it uses at a moment.
Laptops rarely pull full power all the time; usage changes based on tasks and settings.
According to studies, most laptops run between 30 watts and 200 watts under normal use.
The most common average is around 65 watts for everyday tasks like browsing and typing.
Gaming or video editing laptops can exceed 100–180 watts when under heavy use.
However, real‑world users often see much lower average power than the charger’s maximum rating.
Many laptops use far less electricity when browsing or streaming video.
A Reddit user noted that using a power meter showed only 30–40 watts drawn even under active use.
Another message reminded that the wattage label on a charger is the maximum, not constant usage.
Typical Range of Laptop Watt Usage
Laptops vary widely in power draw depending on size, workload, and configuration.
Lightweight and Energy‑Efficient Laptops
Ultrabooks and basic laptops often draw 15–30 watts during simple tasks. These include many small business laptops and Chromebooks designed for basic work.
Mainstream and Everyday Laptops
Most typical laptops (for office work, browsing) use 30–60 watts under normal conditions. This is why many power bricks are around 45–65 watts.
High‑Performance and Gaming Laptops
Powerful laptops with bigger screens, stronger CPUs, and discrete graphics can use 80–150 watts or more under heavy use. Some gaming machines may reach 180–200+ watts when pushed hard.
Display and Accessory Use Adds Power Draw
Displays, USB peripherals, Bluetooth, and Wi‑Fi can add small watts to total consumption.
| Laptop Type | Typical Power (Watts) |
|---|---|
| Small Chromebooks | 10–25 W |
| Basic laptops | 30–60 W |
| Mid‑range laptops | 60–100 W |
| Gaming/Workstation laptops | 100–200+ W |
This shows how usage varies widely by device type.
Daily and Monthly Electricity Use
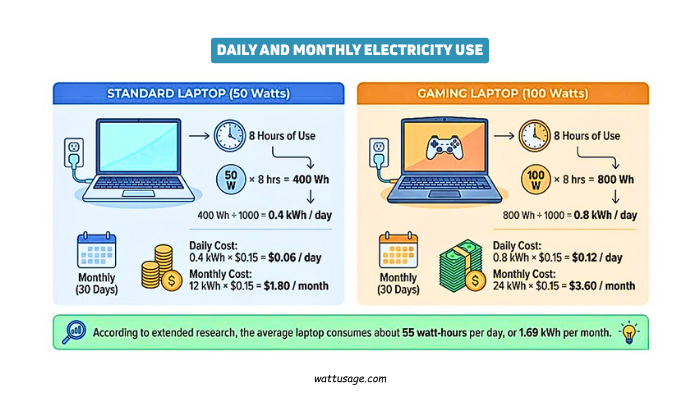
To understand how many watts a laptop use in practical terms, you must consider hours of use.
A laptop drawing 50 watts running for 8 hours uses:
50 W × 8 hrs ÷ 1000 = 0.4 kWh per day
If your electricity rate is $0.15 per kWh, then:
0.4 kWh × $0.15 ≈ $0.06 per day
Monthly (30 days):
0.4 × 30 = 12 kWh monthly therefore $1.80 per month
For a bigger gaming laptop that uses 100 watts for 8 hours:
100 W × 8 hrs = 0.8 kWh/day, $0.12/day therefore $3.60/month
Even heavy daily use only adds a few dollars per month to most bills.
According to extended research, the average laptop consumes about 55 watt‑hours per day, or 1.69 kWh per month.
What Affects Laptop Power Use Most
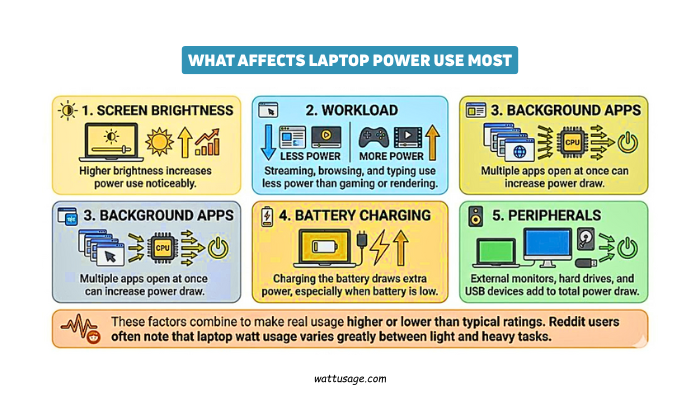
Laptop electricity use is not fixed, it changes with activity and settings:
1. Screen Brightness
Higher brightness increases power use noticeably.
2. Workload
Streaming, browsing, and typing use less power than gaming or rendering.
3. Background Apps
Multiple apps open at once can increase power draw.
4. Battery Charging
Charging the battery draws extra power, especially when battery is low.
5. Peripherals
External monitors, hard drives, and USB devices add to total power draw.
These factors combine to make real usage higher or lower than typical ratings.
Reddit users often note that laptop watt usage varies greatly between light and heavy tasks.
Laptop vs Desktop Power Use
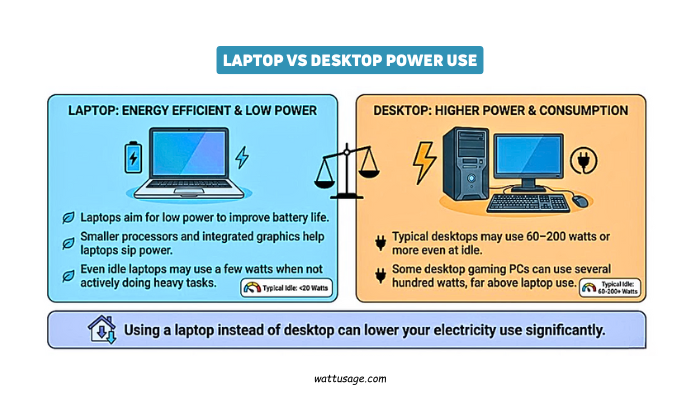
Laptops are far more energy efficient than desktops.
Typical desktops may use 60–200 watts or more even at idle. Laptops aim for low power to improve battery life, so they use less. Smaller processors and integrated graphics help laptops sip power.
Using a laptop instead of desktop can lower your electricity use significantly.
Some desktop gaming PCs can use several hundred watts, far above laptop use.
Even idle laptops may use a few watts when not actively doing heavy tasks.
Real User Experiences
Many laptop owners on Reddit share real power measurements.
One user found their laptop used around 30–40 watts even while plugged in during normal tasks. Another reported that the charger’s maximum rating (like 180W) is rarely fully used unless tasks are very heavy. Some enthusiasts measure usage with power meters, seeing energy use under 100 watts most of the time. These user reports align with research that most laptops don’t draw their maximum rated power constantly.
Estimated Electricity Cost Examples
Here are some approximate monthly electricity cost examples for different laptop usage:
| Laptop Use Case | Consumption (W) | Daily Use (8 hrs) | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Use Laptop | 30 W | 0.24 kWh | $0.04 |
| Everyday Work Laptop | 50 W | 0.40 kWh | $0.06 |
| Media/Streaming | 70 W | 0.56 kWh | $0.08 |
| Gaming Laptop | 100 W | 0.80 kWh | $0.12 |
| Heavy Workstation | 150 W | 1.20 kWh | $0.18 |
Even heavy laptops remain inexpensive relative to most common appliances.
This shows that laptops are cost‑effective in electricity use even if used full workdays.
Ways to Reduce Power Use
Using your laptop more efficiently can reduce energy use:
- Lower screen brightness to save power.
- Use power saver mode when possible.
- Disconnect peripherals when not needed.
- Close unneeded apps to reduce background consumption.
- Hibernate instead of leaving idle to save energy.
These simple steps help keep how many watts a laptop uses low.
Conclusion
So, how many watts does a laptop use depends on type and use.
Most typical laptops draw 30–60 watts during everyday tasks.
High‑performance and gaming laptops can use 100–200 watts or more under heavy load. Daily power use may range from 0.2 to 1.2 kWh depending on usage time and wattage.
Monthly electricity cost for laptop use is only a few dollars even with daily use. Laptops use far less energy than desktops, making them efficient for daily work. Understanding your laptop’s power use helps you balance usage and cost calmly.
Small habits like lowering brightness and using power saver mode make big difference over time.
FAQs
Q1: Do all laptops use the same electricity?
No, lightweight models use less, gaming laptops use more.
Q2: Does battery charging add to power use?
Yes, charging draws extra power when battery is low.
Q3: Is laptop use cheaper than desktop?
Yes, laptops are much more efficient than desktops. UGREEN Official Site
Q4: Can sleep mode save power?
Yes, sleep mode uses very little power.
Q5: Does screen brightness affect watt use?
Absolutely, higher brightness increases power draw.
