PC electricity consumption quietly shapes our daily digital lives.
PC electricity consumption matters because computers now stay on longer than ever.
This topic feels small, yet it touches every bill, habit, and routine Understanding energy use brings calm instead of confusion. A computer feels harmless, but electricity always keeps score. This guide explains power use with clarity and patience.
Understanding PC Electricity Consumption
PC electricity consumption describes how much electrical power a computer uses during operation.
This power changes with tasks, hardware, and daily habits. A simple office computer uses far less energy than a gaming system. Electricity flows differently when a PC rests or works.
Understanding this difference helps control monthly costs.
Desktop computers usually consume more electricity than laptops. They use separate parts that demand constant power. Monitors, processors, and graphics cards all draw electricity together.
Each component quietly adds to overall usage.
PC electricity consumption depends on workload intensity. Writing emails uses less energy than rendering videos. Background apps also increase hidden power usage. Even idle computers consume electricity slowly. This slow drain often goes unnoticed.
Average Power Use of Different PCs
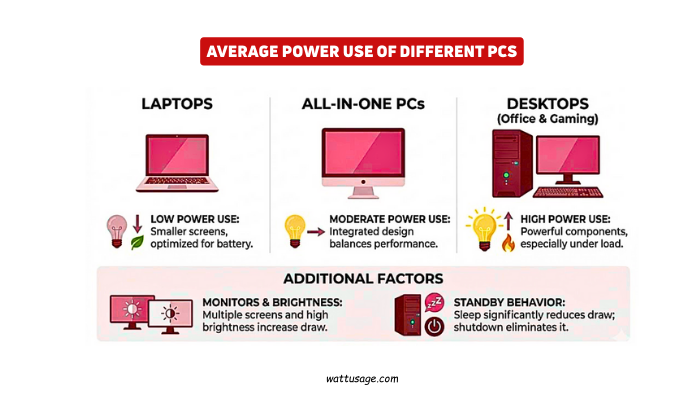
PC electricity consumption varies widely across computer types.
Office desktops usually consume between 150 and 300 watts. Gaming desktops often use 400 to 800 watts. High-end systems may exceed this range during heavy loads.
Laptops consume far less electricity overall. Most laptops use between 30 and 90 watts. Battery charging adds brief power spikes. Smaller screens reduce energy needs significantly.
All-in-one computers balance power and performance. They usually consume between 100 and 250 watts. Their design removes extra components. This keeps electricity use moderate and steady.
PC electricity consumption also includes monitor usage. Large monitors consume 30 to 70 watts. Multiple screens multiply electricity needs. Brightness settings strongly affect monitor energy use.
PC electricity consumption becomes clearer through simple math. A 300-watt desktop running eight hours uses 2.4 kilowatt-hours daily. Monthly usage reaches around 72 kilowatt-hours. Yearly consumption exceeds 850 kilowatt-hours.
At average electricity rates, costs remain manageable. However, longer usage increases expenses steadily. Gaming systems raise costs much faster. Laptops keep electricity spending minimal.
PC electricity consumption also depends on standby behavior. Sleep mode reduces power draw significantly. Shutdown eliminates unnecessary energy use. Leaving PCs on overnight wastes electricity quietly.
Components That Increase Power Usage
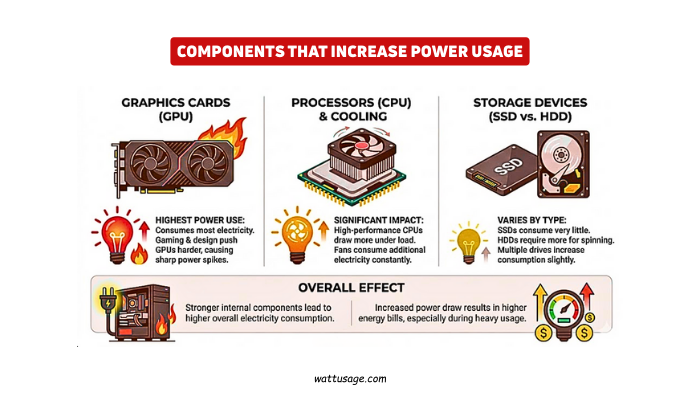
PC electricity consumption rises with stronger internal components. Graphics cards consume the most electricity. Gaming and design tasks push GPUs harder. This causes sharp power spikes.
Processors also impact electricity use. High-performance CPUs draw more power under load. Cooling systems activate more frequently. Fans consume additional electricity constantly.
Storage devices affect energy usage differently. Solid-state drives consume very little power. Hard drives require more electricity for spinning. Multiple drives increase consumption slightly.
Office and Work-From-Home PCs
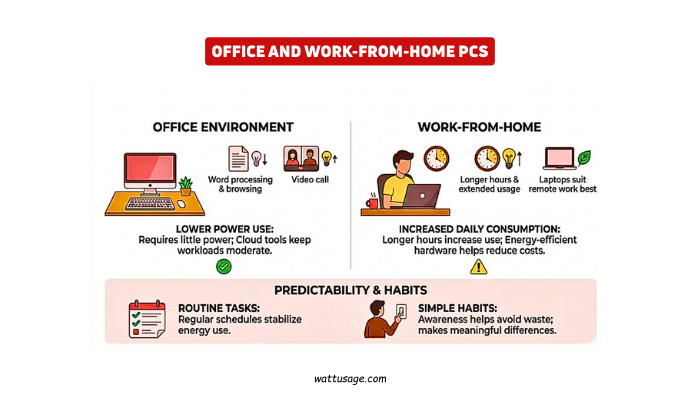
PC electricity consumption stays lower in office environments. Word processing and browsing require little power. Video calls increase usage slightly.
Cloud tools keep workloads moderate.
- Work-from-home routines extend computer usage.
- Longer hours increase daily electricity consumption.
- Energy-efficient hardware helps reduce costs.
- Laptops suit remote work best.
PC electricity consumption becomes predictable with routine tasks. Regular schedules stabilize energy use. Awareness helps avoid unnecessary waste. Simple habits make meaningful differences.
Gaming PCs and Electricity Costs
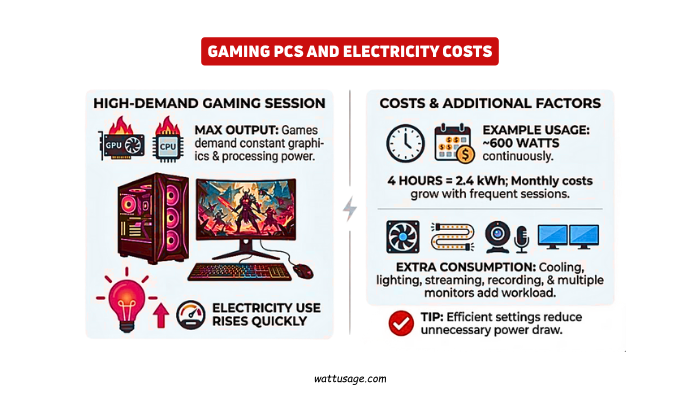
PC electricity consumption feels strongest in gaming systems. Games demand constant graphics and processing power. This pushes components to maximum output. Electricity use rises quickly during gameplay.
A gaming PC may use 600 watts continuously. Four hours of gaming uses 2.4 kilowatt-hours. Monthly costs grow with frequent sessions. Cooling and lighting add extra consumption.
PC electricity consumption also increases with streaming. Recording gameplay adds workload. Multiple monitors raise energy demands. Efficient settings reduce unnecessary power draw.
Reducing PC Electricity Consumption
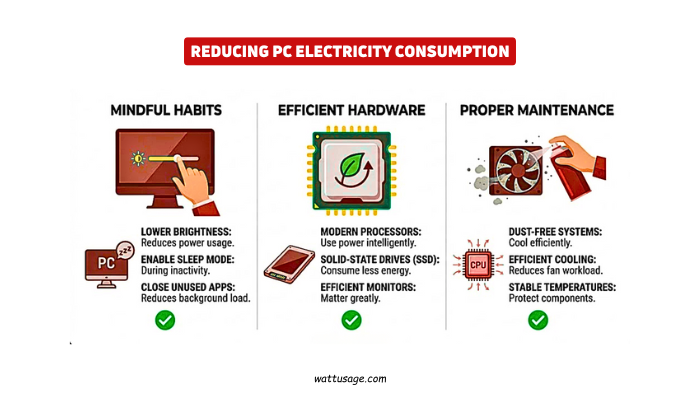
PC electricity consumption can be lowered with mindful habits. Lower screen brightness reduces power usage. Enable sleep mode during inactivity. Close unused background applications.
- Upgrading to efficient hardware saves electricity.
- Modern processors use power intelligently.
- Solid-state drives consume less energy.
- Energy-efficient monitors matter greatly.
PC electricity consumption also drops with proper maintenance. Dust-free systems cool efficiently. Efficient cooling reduces fan workload. Stable temperatures protect components long-term.
Conclusion
PC electricity consumption deserves attention without fear. Understanding power use creates control and clarity. Most computers cost little to operate daily. Habits shape long-term electricity expenses.
Efficient settings reduce waste quietly. Modern hardware balances power and performance. Awareness turns usage into intention. Computers should support life, not drain it.
FAQs
How much electricity does a PC use daily?
Most desktops use 1 to 3 kilowatt-hours daily.
Do gaming PCs consume more electricity?
Yes, gaming systems use significantly more power.
Is leaving a PC on overnight expensive?
Yes, it wastes electricity unnecessarily.
Do laptops save electricity compared to desktops?
Yes, laptops use far less power.
Does sleep mode reduce electricity usage?
Yes, sleep mode greatly lowers consumption.
Curious about PS-5 power consumption? Read our detailed insight to understand its energy use. Click here
